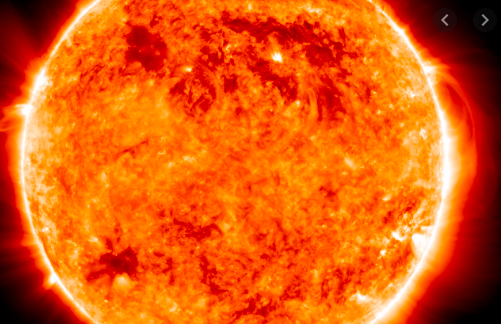
The sun is experiencing a less active phase called 'solar minimum'
The sun is currently experiencing a less active phase, called a solar minimum. The sun goes through regular 11-year intervals including energetic peaks of activity, followed by low points.
During the peak, the sun showcases more sunspots and solar flares. But in a solar minimum, the sun is much quieter, meaning less sunspots and energy.
Some solar scientists believe in the next few decades, we could go into a "Grand Solar Minimum."
The last time this occurred was between 1650 and 1715, during what's known as the Little Ice Age in Earth's Northern Hemisphere, "when combination of cooling from volcanic aerosols and low solar activity produced lower surface temperatures," according to NASA's Global Climate Change blog.
However, scientists say the Grand Solar Minimum won't cause another ice age and that it is likely due to climate change.
They wrote, "The warming caused by the greenhouse gas emissions from the human burning of fossil fuels is six times greater than the possible decades-long cooling from a prolonged Grand Solar Minimum.
"Even if a Grand Solar Minimum were to last a century, global temperatures would continue to warm. Because more factors than just variations in the Sun's output change global temperatures on Earth, the most dominant of those today being the warming coming from human-induced greenhouse gas emissions."
Scientists are aware of the solar minimum due to its regular aspect of the sun's cycle. Sunspots were peaking in 2014, with low points beginning in 2019, according to NASA.
Despite the sun being quiet during the solar minimum, it can be active in other ways, like coronal holes that open in the sun's atmosphere and send out blazing streams of energized particles flying through the solar system on rapid solar wind.
However, these streams of particles during a solar minimum can disrupt the communication and GPS we rely on from satellites.
NASA Sun & Space account shared on Twitter their concerns about the solar minimum.
"The Sun goes through regular cycles of high & low activity. This cycle affects the frequency of space weather events, but it doesn't have a major effect on Earth's climate — even an extended minimum wouldn't have a significant effect on global temperature."
This solar minimum ends solar cycle 24. Early predictions estimated the peak of solar cycle 25 will occur in July 2025, according to the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration.
Source: CNN














Yorumlar